Link to online paper: https://doi.org/10.1128/mSystems.00607-19
Abstract
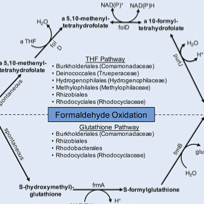
Serpentinization is a low-temperature metamorphic process by which ultramafic rock chemically reacts with water. Such reactions provide energy and materials that may be harnessed by chemosynthetic microbial communities at hydrothermal springs and in the subsurface. However, the biogeochemistry mediated by microbial populations that inhabit these environments is understudied and complicated by overlapping biotic and abiotic processes. We applied metagenomics, metatranscriptomics, and untargeted metabolomics techniques to environmental samples taken from the Coast Range Ophiolite Microbial Observatory (CROMO), a subsurface observatory consisting of 12 wells drilled into the ultramafic and serpentinite mélange of the Coast Range Ophiolite in California. Using a combination of DNA and RNA sequence data and mass spectrometry data, we found evidence for several carbon fixation and assimilation strategies, including the Calvin-Benson-Bassham cycle, the reverse tricarboxylic acid cycle, the reductive acetyl coenzyme A (acetyl-CoA) pathway, and methylotrophy, in the microbial communities inhabiting the serpentinite-hosted aquifer. Our data also suggest that the microbial inhabitants of CROMO use products of the serpentinization process, including methane and formate, as carbon sources in a hyperalkaline environment where dissolved inorganic carbon is unavailable.