Link to online paper: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0048969722025888
Abstract
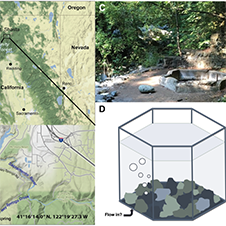
Ney Springs, a continental serpentinizing spring in northern California, has an exceptionally high reported pH (12.4) for a naturally occurring water source. With high conductivity fluids, it is geochemically more akin to marine serpentinizing systems than other terrestrial locations. Our geochemical analyses also revealed high sulfide concentrations (544 mg/L) and methane emissions (83% volume gas content) relative to other serpentinizing systems. Thermodynamic calculations were used to investigate the potential for substrates resulting from serpentinization to fuel microbial life, and were found to support the energetic feasibility of sulfate reduction, anaerobic methane oxidation, denitrification, and anaerobic sulfide oxidation within this system. Assessment of the microbial community via 16S rRNA taxonomic gene surveys and metagenome sequencing revealed a community composition dominated by poorly characterized members of the Izemoplasmatales and Clostridiales. The genomes of these dominant taxa point to a fermentative lifestyle, though other highly complete (>90%) metagenome assembled genomes support the potential for organisms to perform sulfate reduction, sulfur disproportionation and/or sulfur oxidation (aerobic and anaerobic). Two chemolithoheterotrophs identified in the metagenome, a Halomonas sp. and a Rhodobacteraceae sp., were isolated and shown to oxidize thiosulfate and were capable of growth in conditions up to pH 12.4. Despite being characteristic products of serpentinization reactions, little evidence was seen for hydrogen and methane utilization in the Ney Springs microbial community. Hydrogen is not highly abundant and could be consumed prior to reaching the spring community. Other metabolic strategies may be outcompeted by more energetically favorable heterotrophic or fermentation reactions, or even inhibited by other compounds in the spring such as ammonia. The unique geochemistry of Ney Springs provides an opportunity to study how local geology interacts with serpentinized fluids, while its microbial community can better inform us of the metabolic strategies employed in hyperalkaline environments.